All elements of this simulation are licensed under Licence Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Cubic room with diffuse reflection and uniform absorption
Reference
Description
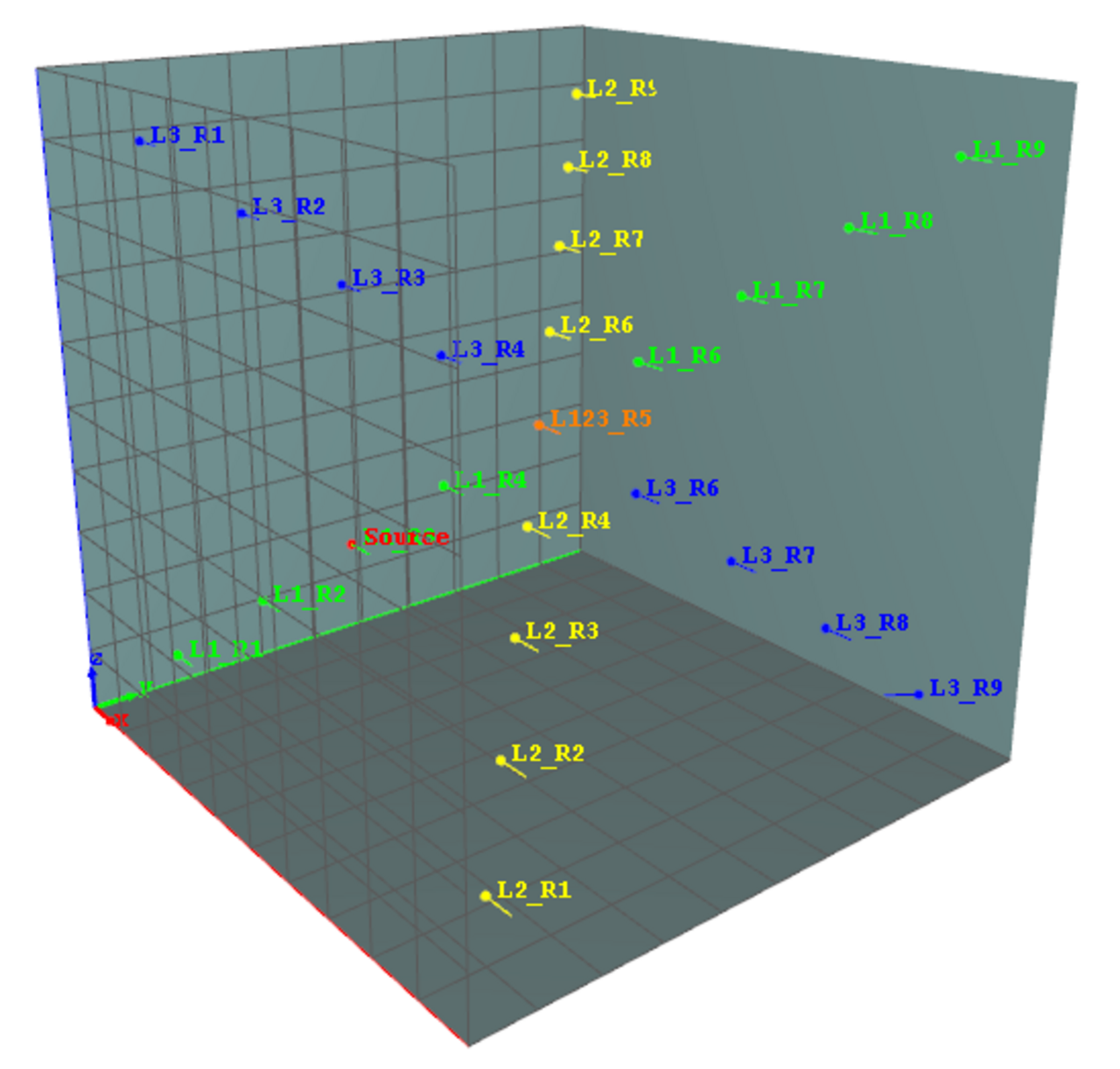
Academic case: Cubic room (10m x 10m x 10m) with 100% diffuse reflection and 20% uniform surface absorption, with a single source at (3,3,3) and 3 lines of 9 punctual receivers along the 3 diagonals of the room.
What is tested?
Comparison between I-Simpa simulations (TCR, SPPS, MD) and data from the radiosity method, as described in [Kang, 2002]. This allows to validate the modelling of the diffuse reflection in SPPS, as well, the behavior of the MD/TCR codes in an ideal diffuse sound field.
[Kang, 2002] Kang, Jian. Acoustics of Long Spaces: theory and design guidance. Thomas Telford, 2002. www.thomastelford.com/books/bookshop_main.asp;
Reference
CAUTION - The following results present comparisons between numerical simulations carried out with I-Simpa and 'reference' data available in the scientific literature.
- It is difficult to prejudge the concept of 'reference'. The deviation between the simulations and the reference data that can be observed do not necessarily call into question the corresponding simulations but can also be associated with other sources of deviation (modeling assumptions, numerical instabilities, experimental uncertainties, etc.).
- Note also that these comparaisons can also show the limitations of some numerical codes.
What is tested? (copie 1)
Comparison between SPPS and data from the radiosity method, as described in [Kang, 2002]. This allows to validate the diffuse reflection in SPPS.
[Kang, 2002] KANG, Jian. Acoustics of Long Spaces: theory and design guidance. Thomas Telford, 2002. www.thomastelford.com/books/bookshop_main.asp;
Description
Academic case: Cubic room (10m x 10m x 10m) with 100% diffuse reflection and 20% uniform surface absorption, with a single source at (3,3,3) and 3 lines of 9 punctual receivers.
Reference

Reference


All elements of this simulation are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Results
Early decay time (EDT) along line 1
This comparison between the EDT calculated with the SPPS and the MD code and those from the reference method (i.e. the radiosity method) shows a very good agreement, with a very small deviation around the location of the sound source. Concerning the TCR code, as expected, the obtained values are identical for all receiver locations. However, in this ideal case (cubic room with diffuse reflection and low/uniform absorption, i.e. the Sabine's assumptions for diffuse field), the TCR code gives relevant results (particularly using the Eyring's formulae).
Early decay time (EDT) along line 2
Here again, regarding the y-scale, a very good agreement is observed between in terms of EDT, between the SPPS/MD/TCR code and the reference method (i.e. the radiosity method).
Early decay time (EDT) along line 3
This figure shows an Inverted behavior between the tested codes and the reference data, i.e. a decrease of the EDT for the reference data, while we observe an increase of the EDT with SPPS/MD. It seems that the line 3 of receivers is reversed between the I-Simpa simulation and the reference data. In this case, if we reverse the line, we observe a perfect agreement.
In addition, it must be note a difference for the receiver 9 between the two SPPS simulations (2008 and 2017), which is due a wrong position of this receiver in the 2008 simulation.
Calculation parameters
Reference
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Active calculation of Atmospheric absorption | NO |
| Active calculation of diffusion by fitting objects | NO |
| Active calculation of direct field only | NO |
| Active calculation of transmission | NO |
| Calculation method | Energetic |
| Limit value of the particle extinction | 5.0 |
| Number of sound particles per source | 1 000 000 |
| Number of sound particles per source (display) | |
| Random initialization number | |
| Receiver radius | 0.31 |
| Simulation length (s) | 2.000 |
| Time step (s) | 0.002 |
Reference
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Active calculation of Atmospheric absorption | NO |
Reference
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Active calculation of Atmospheric absorption | NO |
| Merge with direct field | YES |
| Diffusion equation resolution - Maximum number of iterations | 200 |
| Diffusion equation resolution - Tolerance | 0.000001 |
| Simulation length (s) | 2.000 |
| Time step (s) | 0.001 |